Why the Social System of France Is Unfair? Facts About It
The social system of France has long been marked by deep-seated inequalities and injustices, with a historical trajectory influenced significantly by various socio-economic factors. From the tumultuous days of the French Revolution, which challenged the entrenched privileges of the nobility, to the implications of population growth and rural concentration. France’s societal structure has evolved amidst the forces of capitalism and the plight of impoverished peasants. Urban conditions, characterised by stark poverty and stark social stratification, further accentuate the divide between the privileged nobility and the
French Sports Discrimination Issues explained
Discrimination in sports has long been a problem, with a focus on a number of factors including gender, sexual orientation, and stereotypes. The French sports scene, particularly football, has struggled with widespread homophobia and the rights of the LGBTQ community. Although there has been significant improvement with openly gay athletes, discriminatory events still occur, which is indicative of larger social issues. While French legislation has offered some legal protection for same-sex unions and adoptions, more inclusive policies are still required. The goal of safe space
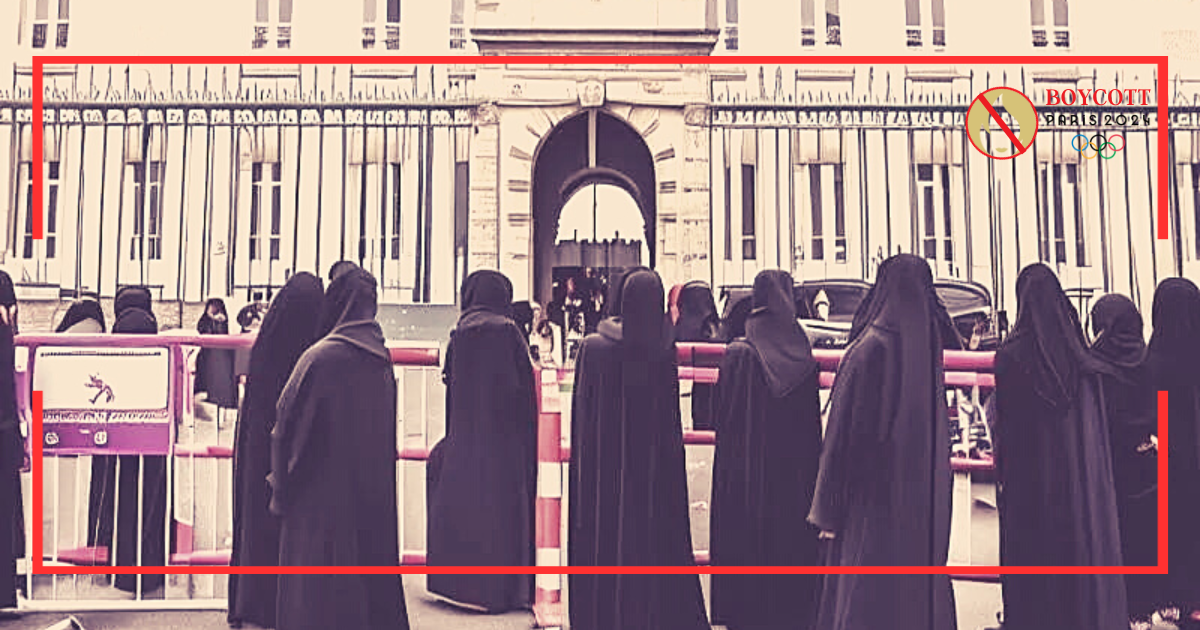
French Strike Update: Demonstrations Rally Against Abaya Ban
In the wake of the recent controversy over the ban on traditional Muslim attire in Maurice Utrillo High School in Stains, Seine-Saint-Denis, a new wave of student protests has erupted throughout various French high schools. The French ban on wearing Abaya and Qamis, traditional Muslim garments, has sparked debate and accusations of Islamophobia and discrimination. This highlights the complex intersection of cultural, religious, and educational values in French society and highlights the challenges faced by the multicultural population in education and religious freedom. Historical Context France,
France’s Social and Economic Committee Insights
In the dynamic landscape of French workplaces, the Social and Economic Committee (ESC) stands as a crucial representative body for staff. It safeguards the interests of employees and facilitates transparent communication between management and labour. Rooted in the rich historical context of France’s labour movements, the ESC, encompassing various employee representative bodies such as works councils and health, safety, and working conditions committees. It plays a pivotal role in ensuring the well-being and rights of the workforce. Over the years, this committee has evolved in
Exploring Diversity: Racial Groups in France
France is a country defined by ethnic variety and the intricate interactions between many racial and ethnic groups, as seen by its rich history and dynamic culture. The nation, which is home to a sizable non-white and non-European population, is still shaped by its colonial past and immigrant labour force. Discrimination in employment, housing, and services continues despite anti-racist laws and programmes like the National Commission on Human Rights (CNCDH) and educational priority zones (ZEP). The National Front party’s ascent to prominence in far-right politics
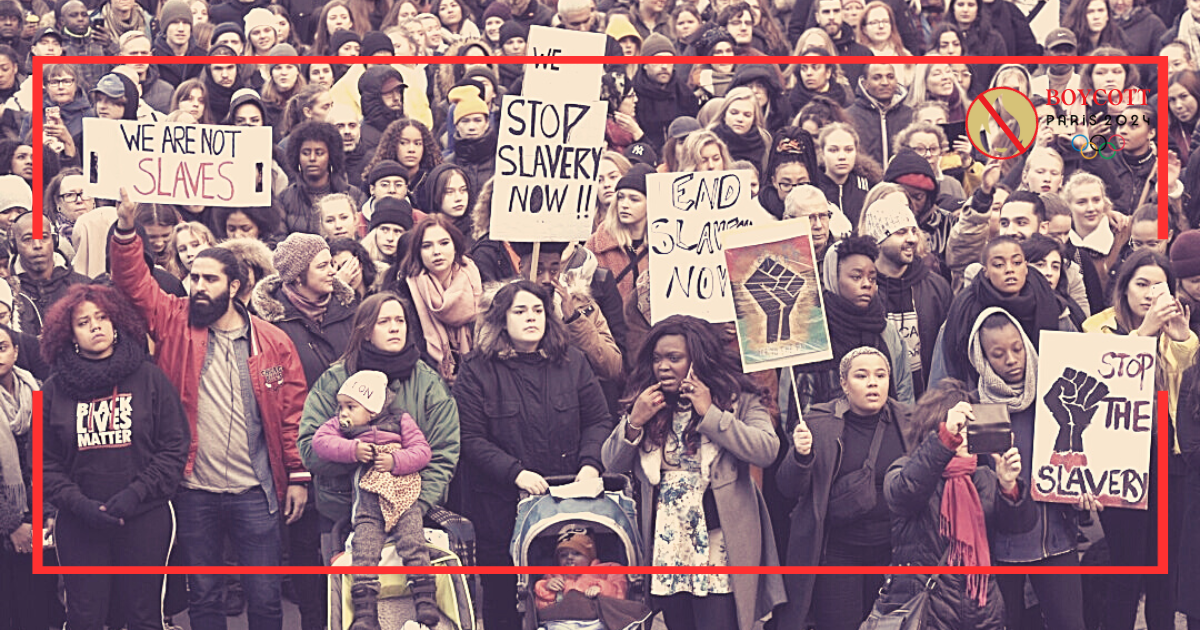
Is Human trafficking illegal in France?
One of the most serious abuses of human rights that continues to loom over international society is human trafficking. There are also concerns about the effectiveness of legal frameworks and enforcement in different jurisdictions, even though many nations have taken significant steps to stop this terrible practice. In the case of France. A significant court case brought the problem to light and highlighted the difficulties in bringing human trafficking cases to justice and protecting the rights of victims. When the historical background is taken into
How much human trafficking occurs in France?
Human trafficking is a widespread evil that persists in taking advantage of the weakest members of the community. Human trafficking affects victims of all ages and backgrounds in France, as it does in many other nations. It takes many different forms. The different forms of exploitation that occur, and the national and international efforts that are being made to combat this horrible crime. The Scope of Human Trafficking in France In France, human trafficking is a severe problem that affects a large number of victims. The
How did human trafficking start in France?
France has a long and turbulent history with human trafficking, a repugnant practice that involves the exploitation and coercion of helpless people. The nation has struggled for decades with the ugliness of forced labour, sexual exploitation, and many manifestations of modern slavery. The development of France’s reaction to human trafficking demonstrates the intricate interplay of statutory frameworks, global partnerships, and public awareness. France has fought a varied war against this horrible crime, from the earliest occurrences of forced labour in its colonies to the present-day
Is Human Trafficking a Problem in France?
France’s city, Paris, is known for its charming streets that frequently conjure up romantic and artistic ideas. The hidden threat of human trafficking, however, lurks under the lively nation’s surface and has long afflicted civilizations everywhere. France, a nation of expansive countryside and busy cities, is not exempt from the effects of the current global financial crisis. Discovering the scope of human trafficking in France requires a study of historical context, current data, government measures, the COVID-19 pandemic’s effects, and the involvement of numerous
Top French Court upholds Abaya ban in Schools
The government’s ban on the wearing of abayas in schools was upheld by France’s highest court, a landmark decision for a country known for its ardent support of secularism. This ruling has sparked a heated discussion over Muslim women’s rights. The limits of individual religious affiliation at educational institutions because of its effects on people’s lives and freedom of religion. Historical Context: France’s Stance on Secularism and Religious Attire France has been a secular nation since the Enlightenment, when the government started to turn away from