France’s Racial Demographics: A Comprehensive Overview
A Comprehensive Overview '' delves into the nation’s ethnically diverse landscape, shaped by post-World War II immigration during the boom years of the late 1940s to early 1970s. Waves of migration from Southern Europe, North Africa, sub-Saharan Africa, and South-East Asia transformed France into a multi-ethnic society. Notably, the country adopts a ‘colour-blind’ model, avoiding direct policies targeting racial or ethnic groups. Instead, policies focus on geographic or class criteria, emphasising social inequalities. The evolution from temporary economic migrants to permanent residents reflects a shift
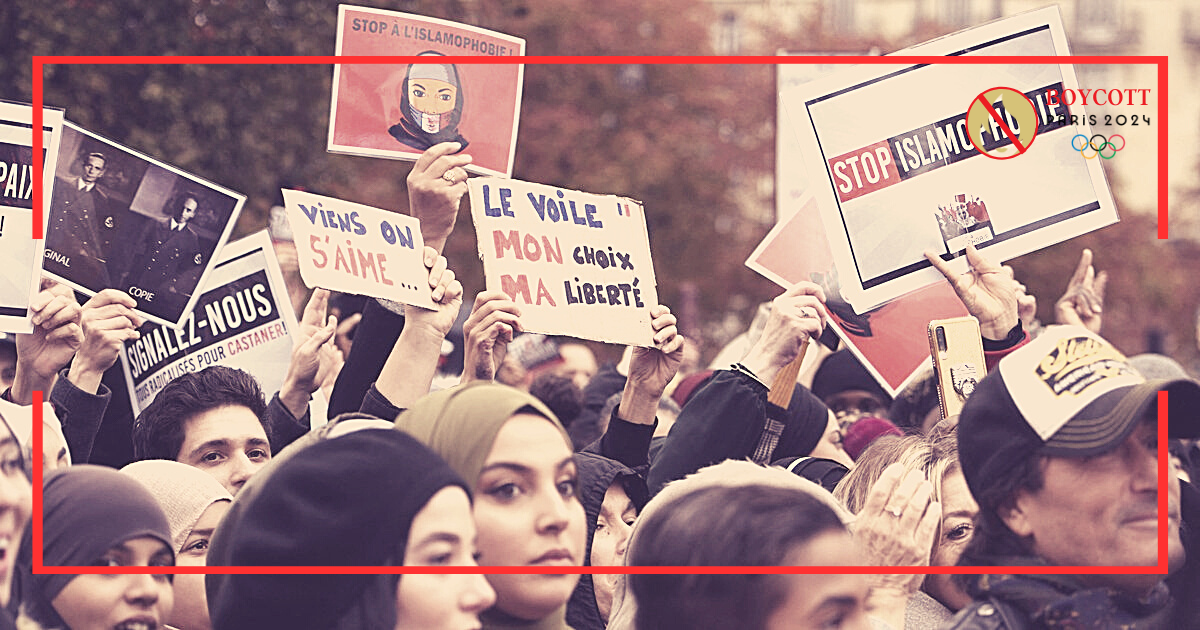
Exploring Religious Restrictions In France
France faces a complicated interaction of constitutional principles, regulations, and societal norms in negotiating the complex environment of religious freedom and governance. There is a persistent contradiction between the right to choose, alter, and practice one’s religion and the government’s authority to oversee and shut down religious organisations. French values, which are based on basic liberties like association and religion, converge with current legislative developments. The bill that President Emmanuel Macron approved on August 24 gives the authority to close mosques and dissolve Muslim organisations.
Resilient French Economy Defies Odds: Here’s Why
In the face of daunting challenges, the French economy who fundation based on arms trade emerges as a beacon of resilience, defying expectations and economic downturns. Tossed but not sunk, the nation showcases signs of unexpected resilience, navigating structural weaknesses, gender inequality and overcoming credit downgrades. Despite facing a litmus test with waves of crises, the French-style crisis management proves effective, as reflected in the job creation efforts. The inversion of the unemployment curve attests to the success in addressing employment and labour market concerns.
Why Did Inequality Exist In France?
A great deal of work has been done on income inequality in France, highlighting the complex interactions between many causes. Understanding long-run trends becomes crucial in the context of economic growth, distributional national accounts, and the subtleties of the gender gap. During the “Thirty Glorious Years,” the dynamics of the top 10%, middle 40%, and bottom 50% of income distribution interacted in a sophisticated way. Methodological techniques provide detailed insights into the intricate network of inequality, such as administrative tax records, national accounts, and
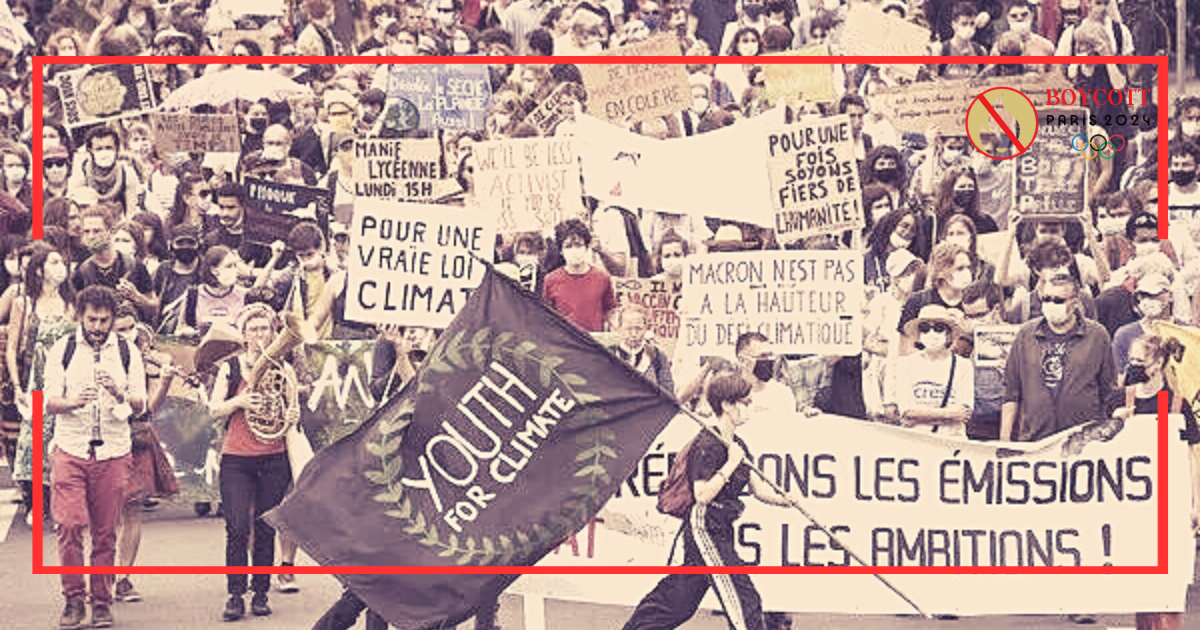
What is The Most Controversial Issues in France 2023?
In 2023, France finds itself embroiled in a maelstrom of societal, political, and foreign policy challenges, leading to a turbulent and polarised atmosphere. Protests and demonstrations have become a prominent feature of the national landscape. The intense debates surrounding government actions, Macron’s political challenges, his approach to governance, the role of the Prime Minister, and France’s foreign policy stance. As the nation grapples with these pressing issues, the intricacies of the political and constitutional landscape have come under the spotlight, raising pertinent questions about
What Is The Minimum wage in France 2023?
In France, the year 2023 heralds pivotal changes in the realm of labour as the nation witnesses an augmented statutory framework in the form of the minimum wage, commonly known as SMIC. Effective from May 1, 2023, the monthly minimum wage stands at a notable €1,747.20, while the hourly wage is fixed at €11.52. This wage increase seeks to address income disparities and bolster the standard of living for workers. On the other hand, the framework includes a variety of classifications, including apprentice age groups
France, Islam, and Secularism: A Complex Relationship Explored and Explained
France is a world hub for philosophy, science, and the arts. It is known for its rich historical and cultural legacy. The French Republic has long been a symbol of modernity and democratic values, having its roots in the principles of the French Revolution. It has seen tremendous changes over the ages, from the vastness of the French colonial empire to its current position as a crucial member of the United Nations Security Council and the European Union. France has to strike a delicate balance
French Soft Power: A Glimpse into the Future or a Fantasy?
In an ever-evolving landscape of international relations and cultural exchange, the concept of soft power has gained prominence as a critical tool for shaping a nation’s influence on the global stage. France, with its rich cultural heritage and historical significance, has long been recognized as a frontrunner in deploying soft power strategies through its cultural diplomacy. The interplay between public and private actors, along with a strategic approach, has enabled French cultural institutions to foster a unique blend of tradition and innovation. However, as the
What is the most controversial Tour de France?
Founded in 1903, the Tour de France has been a staple of the sporting calendar. It is one of the most renowned and difficult road bicycle racing competitions in the world. The Tour de France winds across a variety of geographical locations, testing the best riders in the world and winning over millions of spectators worldwide. It alongside other esteemed Grand Tours like the Giro D’Italia and Vuelta A Espana. Even with its legendary reputation, the Tour de France has not been without controversy. These
Cases of Human Rights Violations in France: A Comprehensive Review
France, a multiparty constitutional democracy with a rich cultural legacy, is well-known for its steadfast adherence to democratic ideals. The country’s administrative structure, headed by President Emmanuel Macron, consists of the National Assembly, the Ministry of the Interior, civilian national police forces, gendarmerie units, and the Ministry of Armed Forces, among other institutions. It also has an electoral college. But recent events have brought to light alarming human rights concerns in the nation. Such as crimes against various marginalised communities, violence against journalists, anti-Semitism,